In the modern eCommerce, pricing is often the deciding factor between a sale and an abandoned cart. If you are running an online store, you likely ask yourself daily: "Is my pricing competitive? Are my rivals undercutting me? Is there room to increase my margins?"
Manually checking competitor websites, opening dozens of tabs, copy-pasting numbers into Excel, and trying to spot trends, is no longer feasible. It is slow, prone to human error, and by the time you finish, the prices may have already changed. This is where price scraping comes in.
Systematic price scraping turns your competitor’s storefront into actionable data. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore how to scrape competitor prices without writing a single line of code.
What is price scraping?
Price scraping is when you use the same data-scraping power to check prices. Instead of going through each product page on the competitor's website and writing down numbers in a spreadsheet, you can use a tool that does it all for you. With one setup, you can see who's charging what, where and when. You won't have to spend time browsing and copying and pasting.
Price scraping tools that are well-built are meant for humans, not developers. They don't use raw HTML or obscure tags. Instead, they give you clean tables and reports: product names, prices, discounts, and timestamps.
Price scraping is easy to mix up with general web crawling, but they serve different purposes. Crawlers are designed to discover and map pages, mostly by reading and following links and code. Search engines use crawlers to understand what's on the web. Price scrapers, on the other hand, skip most of that detail. They go straight for specific pieces of information, like the current price on a product page, and organise those numbers into simple, human-friendly outputs you can actually use.

How to scrape competitor prices without coding with Automa?
To give you an idea, we'll use Amazon, the world's largest e-commerce platform. The following steps show how you can easily monitor competitor prices in just a few steps using Automa's prebuilt templates.
Preparation
Sign up for an Automa account. You can sign up with any email address, or log in directly using your Google or GitHub account.
Download the Automa desktop app and sign in with your newly created account. The following steps are demonstrated using the Windows version as an example.
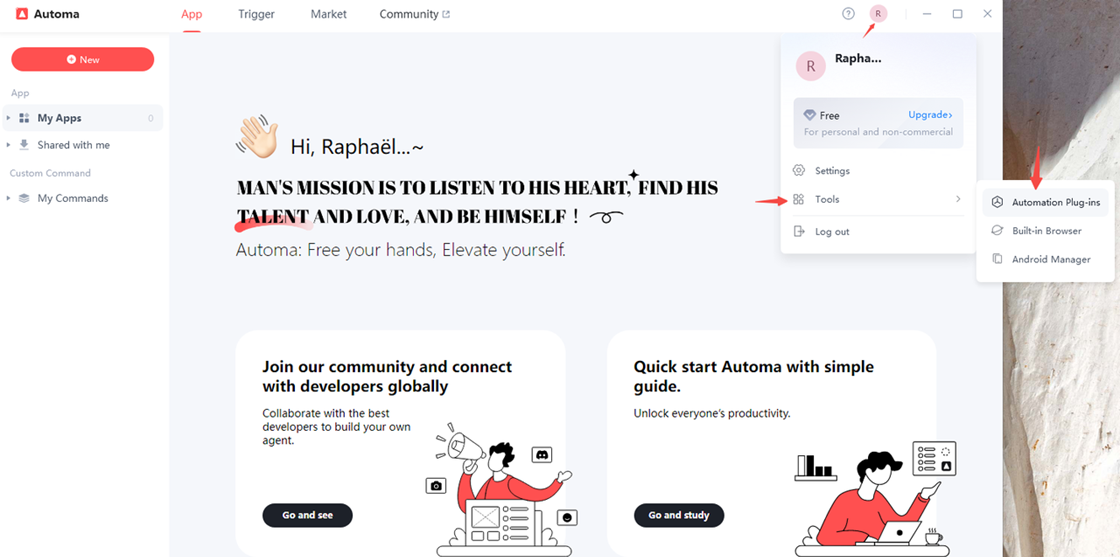
Launch the Automa desktop app and install the Google Chrome Automa extension.
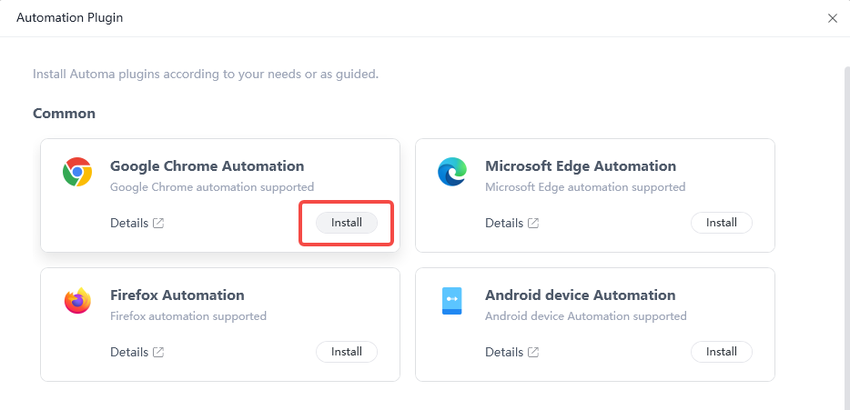
After clicking “Automation Plug-ins,” a pop-up window will appear. Click “Install” to complete the installation of the Google Chrome automation extension.
Next, sign in to your Amazon account in Google Chrome. Everything is now ready—let’s get started with competitor price monitoring.
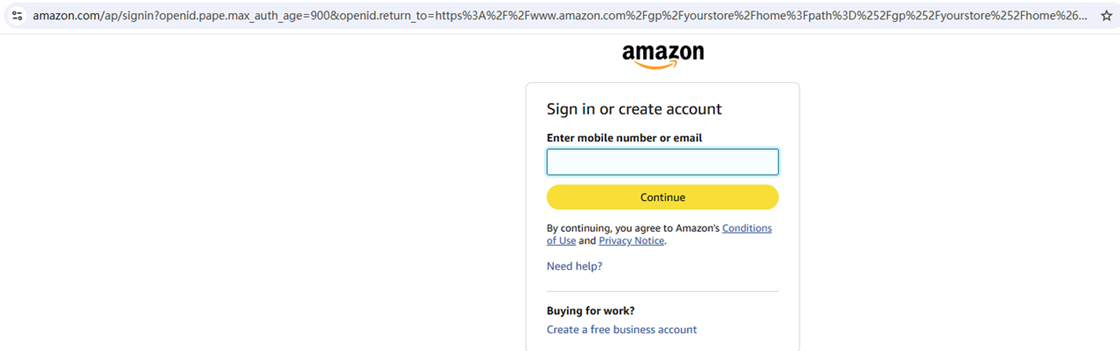
Step 1 Get the Price Scraping Tool from the Automa Marketplace
Click “Login/Register” in the upper-right corner to sign in to your Automa account. Then click “Get,” and the Amazon competitor price scraping tool will be saved to your Automa desktop app.
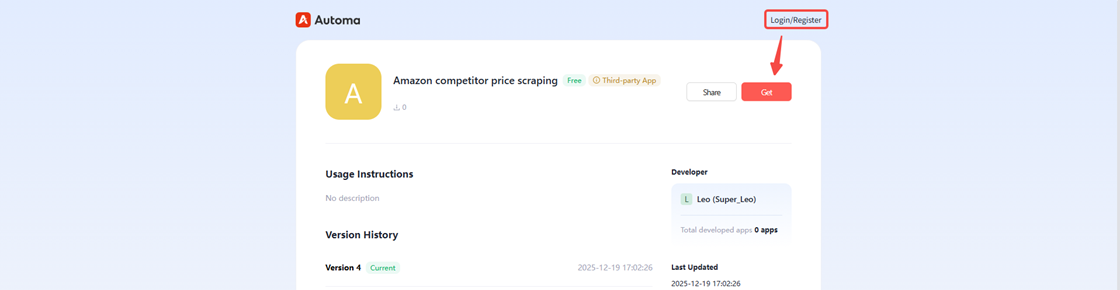
Step 2 Run the Price Scraping Tool in the Automa Desktop App
In the left sidebar, click “Shared with me,” select the Amazon competitor price scraping tool you added, and run it.
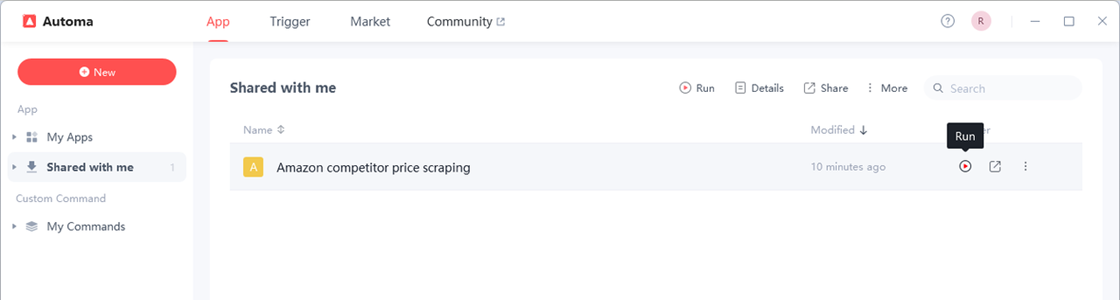
Step 3 Enter the Amazon Product Links You Want to Monitor
When you run the app for the first time, it needs to create a table to store the data. Be sure to select “Yes”.
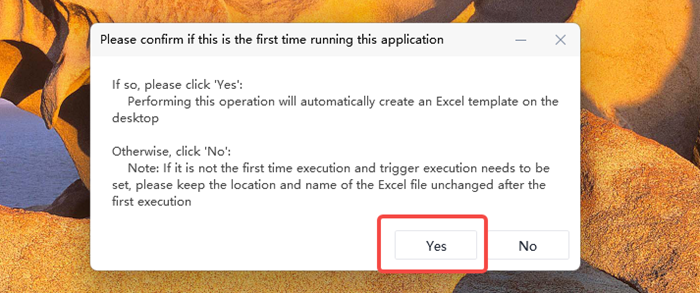
A pop-up window with a table will then appear. Enter the Amazon product links you want to track in column A—there is no limit on the number of links. Finally, click “Done” to start tracking your competitors’ prices on Amazon.
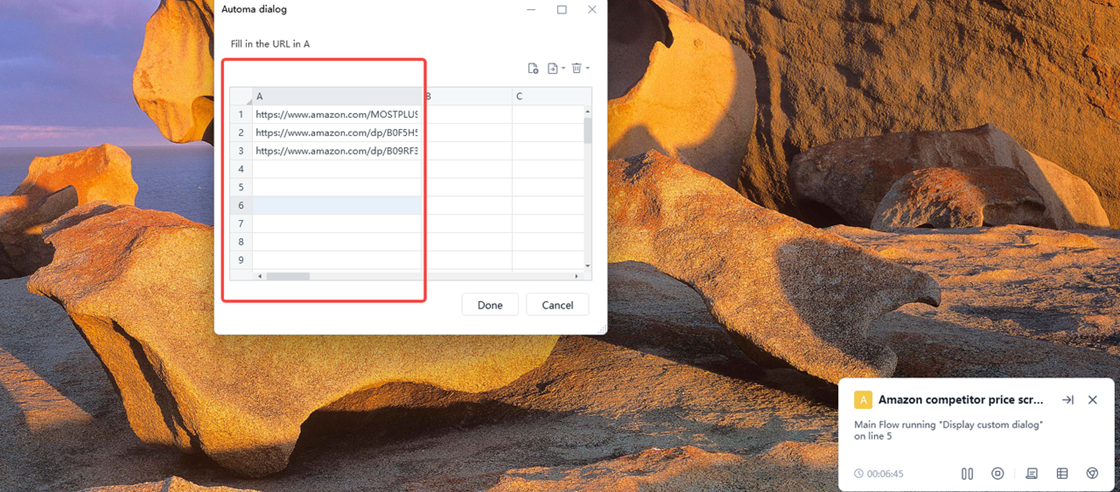
Step 4 Review the Results After Scraping Is Complete
When “Done running” appears in the bottom-right corner, your program has finished. Now, open the file named “competitor_price_scraping” on your desktop to view the results. The spreadsheet includes the URL, ASIN number, title, and the date each data point was scraped.
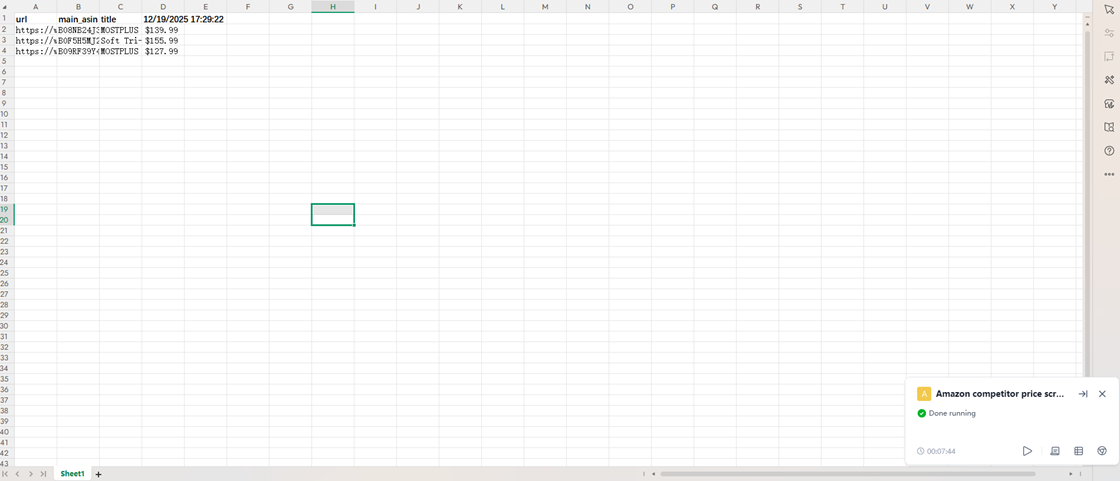
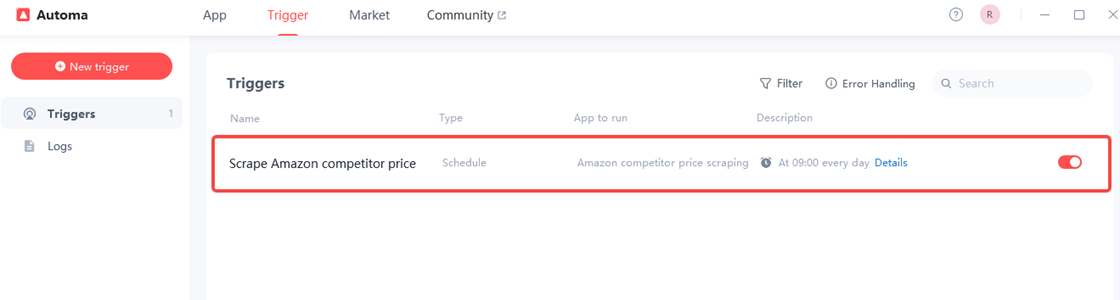
Step 5 Set Up a Trigger
After completing your first price scrape, you may want it to run automatically every day at 9:00 AM to track competitor data. To do this, you need to set up a scheduled trigger. In the Automa desktop app, click “Trigger” in the top navigation bar, then click “New Trigger” and select “Scheduler”.
Now set your trigger schedule. First, give your trigger an easy-to-remember name. Then select the scraping tool named “Amazon competitor price scraping”. Next, in the “Frequency” field, choose how often you want the program to scrape competitor prices—we’ll set it to run once daily. Finally, click “OK” to complete the trigger setup.
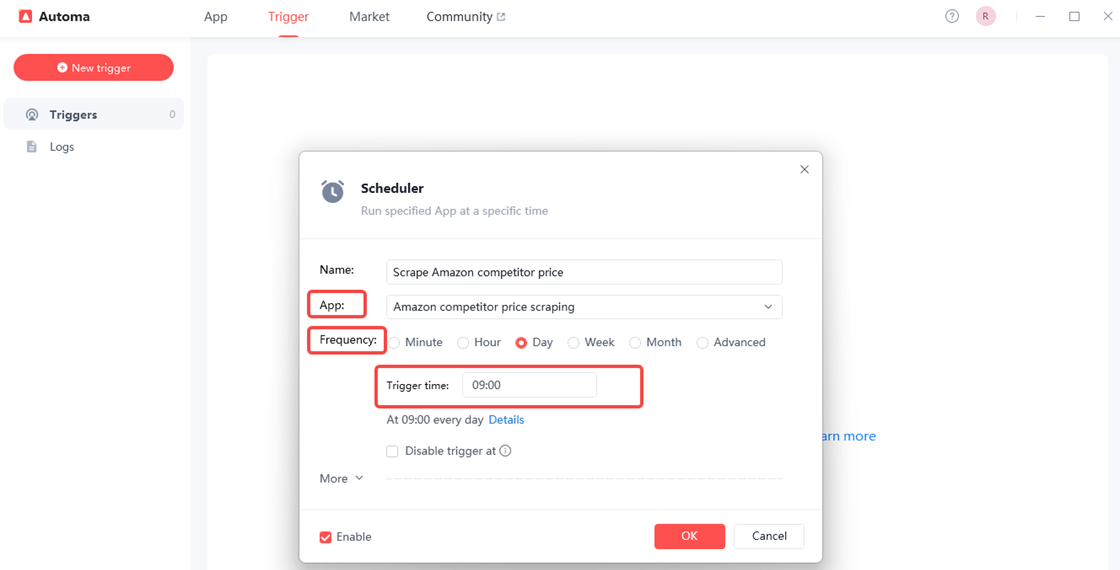
Finally, click “OK” to complete the setup of your trigger.
PS
Do not change the file name or its location.
If you need to add new links, you can simply add them directly in the spreadsheet.
With Automa, you can go beyond price tracking and extend your workflows to Amazon products reviews scraping. By automatically collecting review ratings, review counts, and recent customer comments, you can correlate price changes with customer sentiment, identify quality complaints, and spot feature gaps competitors are struggling with.
Why is price scraping important?
Modern eCommerce is dynamic. Competitors test prices all the time. If you are not tracking them, you are guessing. Systematic price scraping turns your competitor environment into data you can act on. Some practical benefits:
Protect your margins while staying competitive
You do not always have to be the cheapest. But you do need to know when you are too expensive for no reason. Regular competitor price scraping helps you:
Flag products where you are significantly above market
Identify items where you can safely increase price and still stay competitive
Avoid undercutting so heavily that you destroy margins without gaining volume
Win more “in-the-moment” buyers
Customers often sort by price or check a few tabs before clicking “buy.” If your prices are systematically aligned with market levels, you capture more of those impulse decisions.
Support smarter promotions
Price scraping software lets you monitor when others run campaigns like “-20% this week only.” You can then:
Match, beat, or ignore the promo based on your own data
Learn which categories competitors promote most often
Design offers that are different but still attractive
Improve negotiations with suppliers
With reliable pricing data, you can walk into vendor meetings showing how your buy price and competitors’ sell prices line up. This strengthens your case for better wholesale terms or exclusive bundles.

Challenges of price scraping
Price scraping is powerful, but it is not friction-free. Typical issues include:
Dynamic websites
Many eCommerce sites load prices via JavaScript after the page first appears. Basic scrapers that only read HTML may not see the final price. You need tools that can render pages like a real browser or that provide special settings for dynamic content.
Anti-bot systems
Sites increasingly use bot-detection solutions, rate-limiting, and CAPTCHAs. If a tool hits pages too fast from a single IP, requests may start to fail or show incomplete information. Better price scraping software mitigates this using:
Smart throttling
Randomized intervals
IP rotation on paid tiers
Layout changes
A small change in HTML structure can break your extraction rules. Suddenly, your “price” column is empty or filled with the wrong values. To manage this:
Keep scraping rules as generic as possible
Check sample results after major site redesigns
Set basic alerts when extracted prices fall outside expected ranges
Data quality and normalization
Competitors may show prices with different currencies, tax rules, or shipping included. To make scraped data usable, you must:
Normalize currencies and convert when needed
Decide whether to treat “with tax” and “without tax” as comparable
Capture shipping rules or minimum order thresholds when relevant
Competitor price monitoring strategy
Don't just collect data—use it.
Select Key Competitors: Don't track everyone. Focus on the top 3 direct competitors.
Set Frequency: High-volume items (electronics) may need hourly scraping. Niche items may only need weekly checks.
Track Discounts: Capture coupon codes and strike-through prices to understand their promo strategy.
Align Pricing Rules: Decide beforehand—"If Competitor A drops price by 10%, we match up to a limit of $X margin."

Top 6 price scraping use cases
Beyond simple monitoring, how else can you utilize this technology?
MAP (Minimum Advertised Price) Monitoring
If you are a brand manufacturer, you likely have agreements with retailers not to sell your products below a certain price (MAP).
Use Case: Scrape all your authorized retailers daily.
Action: Automatically flag any retailer violating MAP so your sales team can contact them immediately. This protects your brand equity.
Stock Availability Intelligence
Price isn't the only factor; availability is key.
Use Case: Scrape the "Add to Cart" button or "Out of Stock" labels.
Strategy: When a major competitor goes out of stock on a popular item, immediately increase your ad spend for that item. You are now the only option in town, and you can capture their traffic.
Dynamic Pricing Automation
Advanced sellers connect their scraped data directly to their eCommerce platform (Shopify/Magento) via API.
Rule: "If Competitor A is > $50 and In Stock, set my price to $49.99. If Competitor A is Out of Stock, set my price to $54.99."
Ad Spend Efficiency (Smart Bidding)
Running Google Ads or Facebook Ads for products where you are significantly overpriced is a waste of money. Your conversion rate will plummet if users click your ad only to find your competitor selling the same item for 20% less.
Use Case: Connect your scraped price data to your Ad Manager
Strategy: "Pause when Uncompetitive." Set a rule: If my price is >15% higher than the market average, automatically pause ads for this specific SKU. This protects your ROAS (Return on Ad Spend) and ensures you only pay for traffic you can actually convert.
Total Landed Cost Analysis (Shipping & Fees)
A common mistake is scraping only the product price displayed on the collection page. However, customers pay the "Total Landed Cost" (Product + Shipping + Taxes). A competitor might show a lower product price ($19.00) but charge high shipping ($10.00), while you offer it for $25.00 with Free Shipping.
Use Case: Configure your scraper to extract the "Free Shipping Threshold" banner (e.g., "Free Shipping over $50") or shipping estimator costs.
Strategy: Market your "Total Cart Value" advantage. If you know their shipping fees, you can run marketing campaigns like: "Don't pay $10 for shipping at Competitor X. Buy from us for free."
Historical Trend Forecasting & Seasonal Strategy
Price scraping isn't just about "now"; it is about building a timeline. By scraping continuously over time, you build a historical dataset.
Use Case: Analyze how competitors priced their products during major events like Black Friday, Prime Day, or Christmas last year.
Strategy: Predict future moves. If the data shows that Competitor A always drops prices by 15% on the first Monday of November, you can preemptively launch your sale on the preceding Friday to capture the "early bird" shoppers before they do.
Is competitor price scraping legal?
In most places, it's legal to collect public data (like information that's available to everyone) as long as you follow the rules:
No Personal Data: Do not scrape user reviews that contain names or personal info (PII) without consent.
Respect Server Load: Don't send lots of requests to the competitor's website very quickly, as this could cause it to crash.
No Login Barriers: Do not scrape data behind a username/password login unless you have explicit permission.
Copyright: You cannot republish their product descriptions or images as your own (this is called copyright infringement), but you can usually extract the price.
Conclusion
Price scraping is no longer a "secret weapon" for tech giants. It is a fundamental survival skill for modern eCommerce. By using free, no-code, AI automation tool, you can lift the fog of war and see exactly what your market is doing.
Start small. Pick 10 products and one competitor. Build a simple scraper today. The insights you gain in the first week will likely change how you price your products forever. Don't guess—know.
FAQs
How often should I scrape competitor prices?
For most retailers, daily scraping is the standard. However, during holiday seasons (like Black Friday), you may want to scrape multiple times a day, such as per hour.
Can I scrape prices from Amazon and marketplaces with Automa?
Yes. Automa is an AI-driven RPA tool that can imitate how people work to collect information from websites like Amazon, eBay, Shopee, and others. It can open product pages, get the prices, titles and images, and save them to Excel or a database.
Do I need coding skills for reliable price scraping with Automa?
No. Automa is mainly a no-code platform. You can build a scraper using its visual interface: Use drag commands like "Get Element Text" or "Click Element." Or click on the price on the Amazon page to tell the bot what to grab.
How to scrape prices from eCommerce websites with Automa?
Step 1: Open Automa and Create a New Automation
Launch the Automa desktop app
Click Create New Flow / Automation
Choose Web Automation
Step 2: Open the Target eCommerce Website
Use the Open Web Page action
Enter the competitor product or category URL
Wait for the page to fully load
Step 3: Locate and Select the Price Element
Use Automa’s Capture Element tool
Click directly on the price displayed on the page
Save the selector as a variable (e.g., product_price)
Step 4: Handle Product Lists or Pagination
Use Loop / For Each Element to iterate through product cards
Step 5: Normalize and Clean Price Data
Store cleaned values in structured columns
Step 6: Export Data to Excel
Add Write to Excel action