You just spent six figures on a top-tier ERP system. Maybe it’s NetSuite, SAP S/4HANA, or Microsoft Dynamics 365. Yet, your finance team still spends the last week of every month drowning in Excel spreadsheets, manually reconciling invoices. Your inventory data in the warehouse doesn’t match what the sales team sees in the CRM until 24 hours later.
This is the "ERP Paradox." You bought a Ferrari, but you are pushing it uphill.
The problem isn’t the software. It’s the disconnect between your systems and your people. ERP automation is the bridge that fixes this. It is not just about making things faster. It is about removing the human error that bleeds profit margins and turning your ERP from a passive database into an active engine of growth.
This guide is for the CFOs and IT Directors who are done with manual workarounds. We will break down exactly how to build an automation strategy that delivers measurable ROI, minimizes risk, and actually works.
What Is ERP Automation?
At its core, ERP automation is the use of technology—ranging from simple APIs to advanced AI agents—to trigger workflows and synchronize data between your ERP and other business applications without human intervention.
Think of the traditional workflow. A sales rep closes a deal in Salesforce. They email the order details to Finance. A finance manager opens the email, logs into the ERP, and manually types in the invoice data. This is the "Swivel Chair" method. It is slow, expensive, and prone to typos.
Automation replaces that swivel chair with a digital pipeline.
When that deal closes in Salesforce, an automated workflow immediately validates the data, checks inventory levels in the ERP, generates the invoice, and notifies the warehouse. No emails. No typing. No lag.
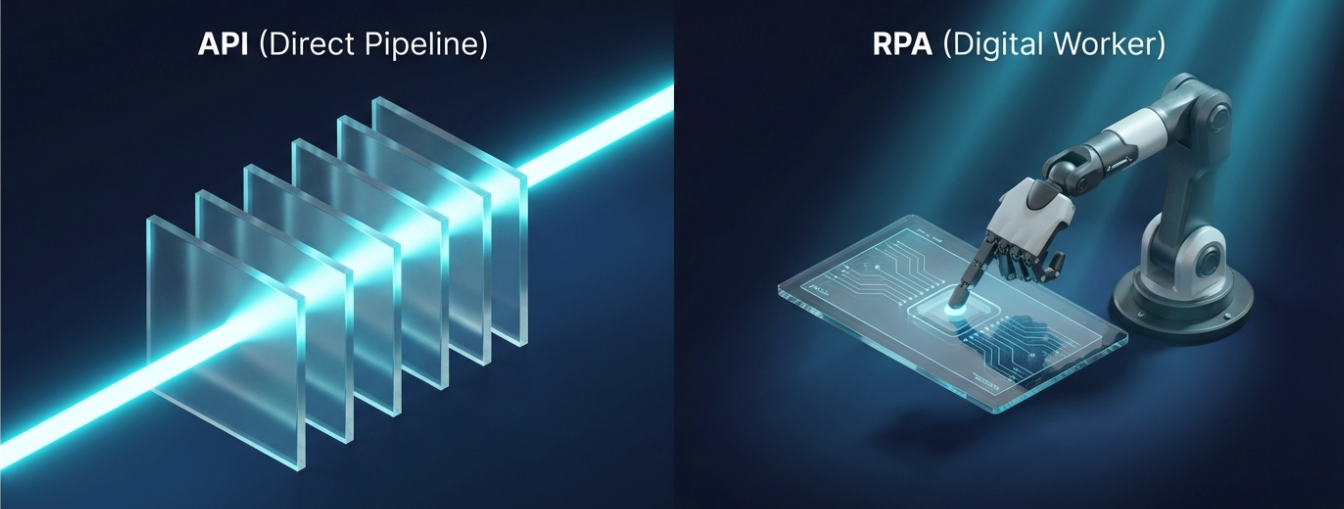
API vs. RPA
To understand automation, you must distinguish the "How."
API (Application Programming Interface): This is a direct pipe between databases. It is fast and stable. For example, using NetSuite’s SuiteTalk to pull data directly from Shopify.
RPA (Robotic Process Automation): This is a "digital worker." If a legacy system lacks an API, a bot mimics human keystrokes to scrape data from the screen. It is slower but necessary for older systems.
But here is a critical distinction often missed. Automation is not just about speed, it is about data integrity. According to a 2021 Gartner report on Hyperautomation, organizations that automate data entry reduce process rework by 30%, directly impacting the bottom line.
Key Benefits of ERP Automation for Your Business
Why should a CFO sign off on the budget for this? It’s not just about "convenience." It’s about survival in a margin-compressed market. Here are the hard, quantifiable benefits.
Reduce Manual Data Entry and Errors
The most immediate impact is the elimination of keystrokes. Manual data entry is the silent killer of productivity. It forces high-level talent to do low-level work.
Consider the cost of correction. It takes 30 seconds to type an invoice line item, but it takes 30 minutes to fix it if the wrong SKU is entered and shipped. By automating the data flow, you stop paying your staff to fix mistakes they shouldn't have made in the first place. You shift their focus from data entry to data analysis.
Break Down Siloed Departments
Departments naturally hoard data. Sales lives in the CRM; Operations lives in the WMS; Finance lives in the ERP. These are siloed departments.
Without automation, these teams only sync up during weekly meetings or via messy email chains. Automation forces these systems to talk. When the marketing team launches a campaign, the ERP should automatically alert procurement to forecast higher material demand. This creates a "Single Source of Truth" that everyone trusts.
Achieve Real Time Reporting and Visibility
You cannot steer a ship if your map is three weeks old. Traditional reporting relies on month-end closes. Real-time reporting changes the game.
With automated data aggregation, a CFO can see the exact cash flow position on a Tuesday morning at 10:00 AM, not just on the 30th of the month. You get visibility into inventory turns, production bottlenecks, and cash runways as they happen. This agility allows for course correction before a small issue becomes a quarterly loss.
Lower Operational Costs and Improve ROI
Let’s talk numbers. ERP automation benefits are measured in ROI.
McKinsey research indicates that current technologies can automate 45% of the activities people are paid to perform. But how do you calculate this for your specific ERP project?
How to Calculate ERP Automation ROI?
Don't guess. Use this formula to justify the investment:
Annual Savings = (Hours spent manually per week × 52 weeks × Hourly Wage) + (Cost of Errors/Rework) ROI = (Annual Savings - Cost of Automation Tool) / Cost of Automation Tool
Example: If your AP clerk spends 20 hours/week manually keying invoices at $30/hour, that costs you $31,200/year. If an automation tool costs $5,000/year and eliminates 90% of that work, your first-year ROI is over 460%.

Real World ERP Automation Examples
Theory is fine, but execution is what matters. Here are specific ERP automation examples where we see the highest impact.
Finance Process Automation
The finance department is usually the best place to start. Specifically, accounts payable automation.
The Scenario: A supplier sends a PDF invoice via email. The Automation:
An AI agent scans the inbox and extracts data using OCR (Optical Character Recognition).
It logs into the ERP and performs a "Three-Way Match" (comparing the Invoice, the Purchase Order, and the Goods Receipt Note).
If everything matches, the payment is scheduled automatically.
If there is a discrepancy, it alerts a human manager.
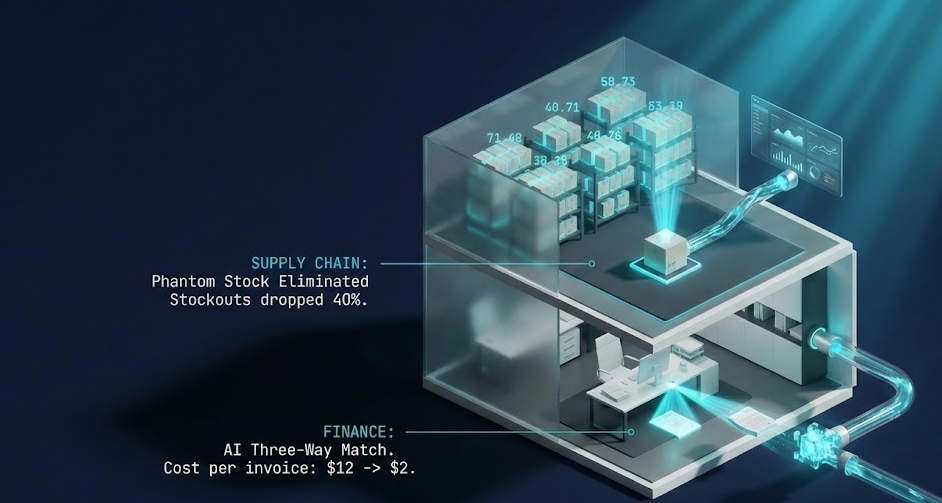
This finance process automation reduces the cost per invoice from roughly $12 (manual) to under $2 (automated).
Supply Chain and Inventory Management
Over-selling stock is a nightmare. Let’s look at a real-world application (anonymized for client privacy).
A mid-sized auto parts manufacturer using NetSuite. They sold on Shopify, Amazon, and B2B direct. Inventory synced only once every 24 hours via a CSV upload. This led to a 15% cancellation rate due to "phantom stock." We implemented an iPaaS middleware to sync inventory in real-time (every 5 minutes). The Result:
Stockouts dropped by 40% in the first quarter.
Customer support tickets related to "Where is my order?" fell by 60%.
The ERP became the true master record for 12,000 SKUs.
Human Resources and Payroll
HR automation ensures that employee data is consistent. When a new hire is added to the HRIS (like BambooHR), automation can create their profile in the ERP for payroll, provision their IT accounts, and set up their expense reporting limits. This eliminates the "onboarding lag" where new employees wait days for system access.
Customer Service and CRM Integration
Your support team needs to know if a customer pays their bills on time. Integrating the ERP with your CRM allows a support agent to see a customer’s credit status, order history, and shipment tracking numbers without leaving their helpdesk software. It empowers them to solve problems in one call, not two.
How to Implement ERP Automation in 5 Steps
Most automation projects fail because they start with tools, not processes. Do not buy a bot and look for a problem. Follow this workflow automation roadmap.
Step 1: Audit Your Current Workflows
Map out your processes. Literally. Draw them on a whiteboard. Identify every point where a human has to copy-paste data. You are looking for high-volume, repetitive, rule-based tasks. If a process requires "gut feeling" or complex judgment, it is not ready for automation yet.
Step 2: Select the Right Automation Tools
There is no one-size-fits-all. Choosing the wrong architecture creates technical debt. Use this decision matrix:
Tool Type | Best For... | Pros | Cons | Examples |
Native Integration | Simple, 1-to-1 connections | Free/Low cost, stable, supported by vendor. | Limited customization. Rigid. | Salesforce to NetSuite Connector. |
iPaaS (Integration Platform) | Complex, multi-app ecosystems | Scalable, central dashboard, handles logic. | Recurring cost, learning curve. | Celigo, Boomi, Workato. |
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) | Legacy systems without APIs | Can automate anything a human does on screen. | Brittle (breaks if UI changes), slower. | UiPath, Microsoft Power Automate Desktop. |
Custom API Scripting | Unique, proprietary workflows | Infinite flexibility. | High maintenance, requires developers. | Python scripts, AWS Lambda. |
Step 3: Clean Your Data Before Migrating
This is the most critical step. If you automate bad data, you just scale your mess.
The Data Governance Checklist:
Standardize Naming: Ensure "ACME Corp" isn't listed as "ACME Inc" in another system.
De-duplicate: Merge duplicate customer and SKU records.
Format Validation: Ensure phone numbers and addresses follow a strict format (e.g., E.164 for phones).
Archive: Move data older than 5 years to cold storage to speed up processing.
Insight from Automa: We advise clients to spend 40% of their project timeline on data governance. It prevents the "Garbage In, Garbage Out" disaster.
Step 4: Pilot with a Single Department
Do not try to boil the ocean. Pick one process—like Expense Reimbursement or PO Generation—and automate that first. Prove the win. Fix the bugs. Get the team comfortable with the new way of working.
Step 5: Scale and Monitor Performance
Once the pilot succeeds, roll it out to other departments. But don't set it and forget it. Automation scripts can break if software UIs change. Set up monitoring alerts to notify IT if a workflow fails.
Challenges and Risks to Avoid
As a strategist, I must be honest about the risks. Automation is powerful, but it is not foolproof.
Dealing with Legacy System Integration
Many older ERPs are "black boxes." They don't have modern APIs. This makes integration difficult. You may need to rely on RPA or custom database middleware. This adds technical debt. Be sure your IT team assesses the "connectability" of your legacy systems before promising results to the board.
Managing Employee Resistance to Change
Your staff will worry that robots are coming for their jobs. The Fix: Frame automation as "promotion," not replacement. Explain that the goal is to remove the boring parts of their job so they can focus on high-value tasks. Involve them in the design process. If they build it, they will use it.
Ensuring Data Security and Compliance
When you move data automatically, you must ensure it is secure. Automated workflows need access credentials (API Keys). If these keys are compromised, a hacker has a backdoor to your ERP. Ensure your automation platform meets SOC 2 Type II and GDPR standards. Never hard-code passwords into scripts.
Future Trends Including AI and Cloud ERP
The landscape is shifting fast. Here is what is coming in 2026.
The Rise of AI in ERP Systems
We are moving beyond simple scripts. AI in ERP means the system can understand context. An AI agent won't just process an invoice. It will flag that the vendor changed their bank account number and alert you to potential fraud.
Machine Learning for Predictive Analytics
Machine learning models will look at your historical ERP data to predict the future. Instead of telling you what you sold last month, the system will tell you what you will sell next month, adjusting procurement orders automatically to optimize cash flow.
Hyperautomation and IoT Connectivity
Cloud ERP systems will connect directly to machines. In manufacturing, IoT sensors on the production line will feed real-time performance data into the ERP (like SAP S/4HANA), triggering maintenance tickets automatically before a machine breaks down.
Conclusion
ERP automation is no longer a luxury for Fortune 500 companies. It is a necessity for any business that wants to scale without drowning in overhead.
The choice is simple. You can continue to pay your smart people to do dumb work, or you can build a system that runs itself. The technology is ready. The question is, are you?
Ready to stop the manual madness? Don't guess where to start. Use the Automa Workflow to identify your biggest bottlenecks and see exactly how much time and money you could save in the next 30 days.
Frequently Asked Questions
What processes should I automate first?
Start with "High Volume, Low Complexity" tasks. Accounts Payable (invoice processing), Employee Onboarding, and Order Entry are the classic "quick wins" that deliver immediate ROI.
How much does ERP automation cost?
It varies wildly. A simple native connector might cost $100/month. A full enterprise iPaaS implementation can range from $20,000 to $100,000+ annually depending on data volume and complexity.
Does ERP automation require coding?
Not always. Modern "Low-code/No-code" platforms like Zapier or Workato allow business analysts to build workflows using drag-and-drop interfaces. However, complex data transformations usually require some technical expertise.
Is ERP automation the same as RPA?
No. RPA (Robotic Process Automation) is just one tool used within ERP automation. RPA mimics human clicks on a screen. True ERP automation also uses APIs, native integrations, and AI to move data at the database level, which is faster and more stable.
How long does implementation take?
A simple workflow (like syncing leads to ERP) can take 2 weeks. A full-scale financial transformation usually takes 3 to 6 months. It depends heavily on the cleanliness of your data.

